PID
PID stands for Photo Ionization Detector and can detect Volatile Organic Components in short VOC's. All VOC's are described below. The PID-value is measured with a PID-meter in parts per million. It is used directly after drilling or to measure the air in the samples. A PID-meter can't measure the type of VOC present only the amount present of that type of VOC. So to use this device some pre-investigation is necessary.
Method
With the help of diffusion or a pump the gas enters the PID-meter. In the PID-meter the gas is exposed to high energetic photons. These photons cause the gas to lose an electron which makes the gas particles positively loaded ions. These ions generate an electric current. This current is translated to the amount of gas present by the PID-meter.
Ionization potential
To activate the gas an electric charge is needed to extract an electron from the gas. This charge varies with the type of gas present and is expressed in Electron Volts. The minimal amount of electron volt needed is called the ionization potential. With the PID-meter one has three choices the 9.8 eV, the 10,6 eV and the 11.7 eV lamp. The higher the amount of charge the more types of gasses can be detected. On the right there is a graphical display of the type of gasses and their activation charge.
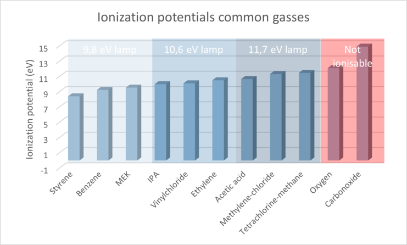
Apart from this ionization potential most of the times also a correction factor is known. This factor can be used when one suspects that only one type of gas is present in the field. By applying the correction factor on the PID-meter the concentration detection becomes more accurate. If the correction fact is not used the PID-meter does a wide spectrum measurement calibrated with isobutylene.
References