Diorite
Diorite is a coarse-grained intrusive rock that is mainly composed of plagioclase feldspar and amphibole minerals which give it its light to dark grey color. Diorite forms at places where volcanoes are formed due to convergent plate boundaries between continental and oceanic plates. Diorite is the intrusive version of andesite.
Characteristics
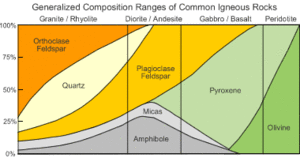 Diorite is usually composed of sodium-rich plagioclase with lesser amounts of hornblende, biotite, and pyroxene minerals. It usually contains little if any quartz. This makes diorite a coarse-grained rock with a contrasting mix of black and white mineral grains.
Diorite is usually composed of sodium-rich plagioclase with lesser amounts of hornblende, biotite, and pyroxene minerals. It usually contains little if any quartz. This makes diorite a coarse-grained rock with a contrasting mix of black and white mineral grains.
Environment
As mentioned before is diorite the intrusive variant of andesite. Both rocks form above subduction zones of the continental crust. They often form after an oceanic plate melts during its decent into the subduction zone to produce a source of magma.
Diorite is a coarse-grained igneous rock that forms when the magma remains below Earth's surface and cools slowly. Slow cooling facilitates the growth of large mineral crystals in the rock. Andesite is a fine-grained rock that forms when the magma erupts onto the surface and crystallizes quickly.
Andesite and diorite have a composition that is intermediate between basalt and granite. This is because their parent magmas formed from the partial melting of a basaltic oceanic plate. This magma may have received a granitic contribution by melting granitic rocks as it ascended or mixed with granitic magma.[1]
Micro-diorite
 Micro-diorite is a medium-grained intrusive igneous rock. It contains crystals that are smaller than grains of rice, which are interlocking and randomly oriented. It is dark grey or greenish brown.
Micro-diorite is a medium-grained intrusive igneous rock. It contains crystals that are smaller than grains of rice, which are interlocking and randomly oriented. It is dark grey or greenish brown.
Like diorite, micro-diorite forms from magmas that do not contain much quartz (silica) or the light colored minerals that make up granite. The crystals are smaller than those in Diorite, indicating that the magma cooled more quickly.
It usually occurs as small intrusions called ‘dykes’, which are sheet-like and cut through the surrounding rocks.
References
Diorite

| Type | Intrusive igneous rock |
|---|---|
| Clasts | Coarse grained |
| Hardness | Very hard |
| Color | Light to dark grey |
| Minerals | Plagioclase feldspar and amphibole minerals |
| Touch | Rough |
| Image | Diorite |